[翻译]Sol - 从零开始的MQTT broker - 第四部分:数据结构
原文 Sol - An MQTT broker from scratch. Part 4 - Data structures
前言
在继续实现所有的 handler 之前,我们先设计和实现一些最常用的数据结构,包括 哈希表(hashtable),列表(list) 和 **特里树(trie)**。
特里树 不是我们当前就用到的东西,但是在我们后续处理 主题 时会用到他。
也许实现这些数据结构这件事情对于我们这个项目来说有点过于底层了,也确实有很多成熟的实现可以拿来用。但是我个人比较喜欢在稍微有些规模的项目中自己实现数据结构,一方面是这样方便于之后随着项目需求对这些数据结构进行改进,另一方面是,实现数据结构的过程也确实是一个非常好的学习和探索的机会。
哈希表
让我们从一个简单的哈希表开始,哈希表本质上是一个数组,他使用哈希值(下图中的Hashval % Bucketsize)作为存储我们信息的索引,并且试图尽可能的减少冲突情况(例如两个key计算出了同样的哈希值)。
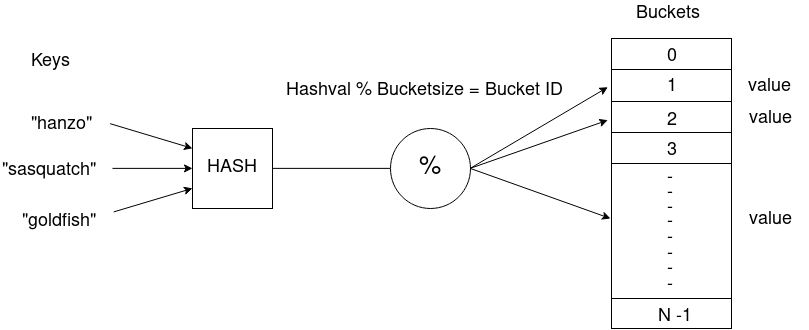
Buckets 是一个数组,一般情况下会是个动态扩容的数组,他通过 key 来关联存储的数据。
src/hashtable.h#include <stdio.h> #include <stdint.h> #include <stdbool.h> // 状态码 #define HASHTABLE_OK 0 #define HASHTABLE_ERR 1 #define HASHTABLE_OOM 2 #define HASHTABLE_FULL 3 // 哈希表条目 // key 键 // val 存储的值 // taken 表示此索引是否已经被占用, 如果是则使用 index + 1 的位置存储 struct hashtable_entry { const char *key; void *val; bool taken; }; // 哈希表结构体, 包括最大尺寸、当前尺寸以及存储的数据 typedef struct hashtable HashTable; // 创建哈希表的函数 // 可以传入一个析构函数指针, 作为删除条目时释放资源的函数 // 如果资源比较简单(基础类型或数据流), 可以传NULL, 可以采用默认函数释放 HashTable *hashtable_create(int (*destructor)(struct hashtable_entry *)); // 通过对每个条目调用 `destructor` 来释放所有资源 void hashtable_release(HashTable *); // 哈希表当前大小 size_t hashtable_size(const HashTable *); // 查看哈希表中是否已经存在此key int hashtable_exists(HashTable *, const char *); // 插入数据, const char * 作为 key, void * 作为 value int hashtable_put(HashTable *, const char *, void *); // 通过 key 获取数据 void *hashtable_get(HashTable *, const char *); // 通过 key 删除数据 int hashtable_del(HashTable *, const char *); // 迭代所有的键值对, 使用传入的函数指针进行处理 int hashtable_map(HashTable *, int (*func)(struct hashtable_entry *)); // 迭代所有的键值对, 使用传入的函数指针进行处理, 并且可以额外传入一个参数 int hashtable_map2(HashTable *, int (*func)(struct hashtable_entry *, void *), void *);
我们通过 typedef struct hashtable HashTable; 这种方式将实际的哈希表的结构封装到的 .c 文件里,这样可以避免哈希表的使用者不使用我们提供的函数,而是直接访问我们的哈希表。这种方式可以被看作是c语言中的私有类。
src/hashtable.c#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <assert.h> #include "util.h" #include "hashtable.h" // 哈希表结构 struct hashtable { // 最大容量 size_t table_size; // 当前数据量 size_t size; // 析构函数指针 int (*destructor)(struct hashtable_entry *); // 条目数组 struct hashtable_entry *entries; }; const int INITIAL_SIZE = 4; const int MAX_CHAIN_LENGTH = 8; const unsigned long KNUTH_PRIME = 2654435761; static unsigned long crc32(const uint8_t *, unsigned int); // 通过输入的key 计算其在哈希表中的序号 // 此处仅进行数字运算, 不考虑冲突情况 static uint64_t hashtable_hash_int(HashTable *m, const uint8_t *keystr) { assert(m && keystr); uint64_t key = crc32(keystr, strlen((const char *) keystr)); /* Robert Jenkins' 32 bit Mix Function */ key += (key << 12); key ^= (key >> 22); key += (key << 4); key ^= (key >> 9); key += (key << 10); key ^= (key >> 2); key += (key << 7); key ^= (key >> 12); /* Knuth's Multiplicative Method */ key = (key >> 3) * KNUTH_PRIME; return key % m->table_size; } // 通过输入的key 计算其在哈希表中的序号 // 此处考虑了冲突情况 // 如果哈希表已经满了, 返回 -HASHTABLE_FULL static int hashtable_hash(HashTable *table, const uint8_t *key) { assert(table && key); // 用量超过总额的 1/2 视为满 if (table->size >= (table->table_size / 2)) return -HASHTABLE_FULL; // 计算序号 uint64_t curr = hashtable_hash_int(table, key); char *k, *currk; // 避免序号冲突的情况 // 最大重复 MAX_CHAIN_LENGTH 次 // 意味着视冲突情况, key 被保存在 curr ~ curr + MAX_CHAIN_LENGTH 这个范围中某一点 for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CHAIN_LENGTH; i++) { // 序号未被占用直接返回 if (table->entries[curr].taken == false) return curr; k = (char *) table->entries[curr].key; currk = (char *) key; // 传入的 key 已存在的情况, 返回相同 key 的序号 if (table->entries[curr].taken == true && STREQ(k, currk, strlen(k)) == true) return curr; curr = (curr + 1) % table->table_size; } return -HASHTABLE_FULL; } // 扩容, 容量 * 2, 重新排布所有的内容 static int hashtable_rehash(HashTable *table) { assert(table); size_t old_size; struct hashtable_entry *curr; // 新数组空间 struct hashtable_entry *temp = calloc(2 * table->table_size, sizeof(*temp)); if (!temp) return -HASHTABLE_ERR; // 暂存旧数组 curr = table->entries; // 指向新数组 table->entries = temp; // 记录空间扩容 old_size = table->table_size; table->table_size = 2 * table->table_size; table->size = 0; int status; // 重新排布所有条目 for (size_t i = 0; i < old_size; i++) { if (curr[i].taken == false) continue; // 也很简单, 就是直接用 put 重新放一遍 if ((status = hashtable_put(table, curr[i].key, curr[i].val)) != HASHTABLE_OK) return status; } // 释放旧数组 free(curr); return HASHTABLE_OK; } // 默认的释放条目函数 static int destroy_entry(struct hashtable_entry *entry) { if (!entry) return -HASHTABLE_ERR; // 释放 key if (entry->key) free((void *) entry->key); // 释放 val if (entry->val) free(entry->val); return HASHTABLE_OK; } // 创建一个空的哈希表 // 新创建的哈希表被分配到堆中, 用完后必须手动释放 HashTable *hashtable_create(int (*destructor)(struct hashtable_entry *)) { // 创建哈希表 HashTable *table = malloc(sizeof(HashTable)); if(!table) return NULL; // 初始化条目数组 table->entries = calloc(INITIAL_SIZE, sizeof(struct hashtable_entry)); if(!table->entries) { hashtable_release(table); return NULL; } // 选择析构函数 table->destructor = destructor ? destructor : destroy_entry; // 初始化数据 table->table_size = INITIAL_SIZE; table->size = 0; return table; } // 当前数据量 size_t hashtable_size(const HashTable *table) { return table->size; } // 是否存在 key int hashtable_exists(HashTable *table, const char *key) { void *ret = hashtable_get(table, key); return !ret ? 0 : 1; } // 添加数据, 如果 key 的哈希值重复则序号 +1 int hashtable_put(HashTable *table, const char *key, void *val) { assert(table && key); // 获得可以存储的序号 int index = hashtable_hash(table, (const uint8_t *) key); // 如果满了 while (index == -HASHTABLE_FULL){ // 尝试扩容 if (hashtable_rehash(table) == -HASHTABLE_ERR) return -HASHTABLE_ERR; index = hashtable_hash(table, (const uint8_t *) key); } // 放置内容 table->entries[index].val = val; table->entries[index].key = key; // 标记使用, 如果是新增, 还需要添加计数 if (table->entries[index].taken == false) { table->entries[index].taken = true; table->size++; } // 译者觉得这里有一个问题, 当 put 使用了重复的 key 时, index会是这个 key 实际存放的索引 // 之后对 key 和 val 进行了赋值, 但是如果 key 是存在的, 那么原来 entry 中的 key 和 val 没有被释放 return HASHTABLE_OK; } // 通过key获得val void *hashtable_get(HashTable *table, const char *key) { assert(table && key); // 查 key 哈希值对应的索引 uint64_t curr = hashtable_hash_int(table, (const uint8_t *) key); // 查 key 实际对应的索引 for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CHAIN_LENGTH; i++){ if (table->entries[curr].taken == true) { if (STREQ(table->entries[curr].key, key, strlen(key)) == true) return table->entries[curr].val; } curr = (curr + 1) % table->table_size; } return NULL; } // 删除一个条目 int hashtable_del(HashTable *table, const char *key) { assert(table && key); // 哈希值对应的索引 uint64_t curr = hashtable_hash_int(table, (const uint8_t *) key); // 找到实际 key 的索引 for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CHAIN_LENGTH; i++) { // 有数据 if (table->entries[curr].taken == true) { // 且 key 一致 if (STREQ(table->entries[curr].key, key, strlen(key)) == true) { // 标记无数据 table->entries[curr].taken = false; // 记录尺寸 table->size--; // 使用析构释放 table->destructor(&table->entries[curr]); return HASHTABLE_OK; } } curr = (curr + 1) % table->table_size; } // 未找到数据 return -HASHTABLE_ERR; } // 通过传入的func迭代哈希表中的所有内容 int hashtable_map(HashTable *table, int (*func)(struct hashtable_entry *)) { assert(func); // 空表不处理 if (!table || table->size <= 0) return -HASHTABLE_ERR; // 就遍历 for (size_t i = 0; i < table->table_size; i++) { if (table->entries[i].taken == true) { // 处理data struct hashtable_entry data = table->entries[i]; int status = func(&data); // 要求传入函数正确时返回 HASHTABLE_OK if (status != HASHTABLE_OK) return status; } } return HASHTABLE_OK; } // 另一个迭代器, 支持一个参数 int hashtable_map2(HashTable *table, int (*func)(struct hashtable_entry *, void *), void *param) { assert(func); if (!table || table->size <= 0) return -HASHTABLE_ERR; for (size_t i = 0; i < table->table_size; i++) { if (table->entries[i].taken == true) { // 区别就是带了参数 struct hashtable_entry data = table->entries[i]; int status = func(&data, param); if (status != HASHTABLE_OK) return status; } } return HASHTABLE_OK; } // 使用预定义的析构函数释放哈希表 // 如果没有定义析构函数, 则使用默认函数 destroy_entry void hashtable_release(HashTable *table){ if (!table) return; hashtable_map(table, table->destructor); if (!table || !table->entries) return; free(table->entries); free(table); } /* The implementation here was originally done by Gary S. Brown. Slighltly * modified by Pete Warden, without any imposition on the reuse of the code. */ /* ============================================================= */ /* COPYRIGHT (C) 1986 Gary S. Brown. You may use this program, or */ /* code or tables extracted from it, as desired without restriction. */ /* */ /* First, the polynomial itself and its table of feedback terms. The */ /* polynomial is */ /* X^32+X^26+X^23+X^22+X^16+X^12+X^11+X^10+X^8+X^7+X^5+X^4+X^2+X^1+X^0 */ /* */ /* Note that we take it "backwards" and put the highest-order term in */ /* the lowest-order bit. The X^32 term is "implied"; the LSB is the */ /* X^31 term, etc. The X^0 term (usually shown as "+1") results in */ /* the MSB being 1. */ /* */ /* Note that the usual hardware shift register implementation, which */ /* is what we're using (we're merely optimizing it by doing eight-bit */ /* chunks at a time) shifts bits into the lowest-order term. In our */ /* implementation, that means shifting towards the right. Why do we */ /* do it this way? Because the calculated CRC must be transmitted in */ /* order from highest-order term to lowest-order term. UARTs transmit */ /* characters in order from LSB to MSB. By storing the CRC this way, */ /* we hand it to the UART in the order low-byte to high-byte; the UART */ /* sends each low-bit to hight-bit; and the result is transmission bit */ /* by bit from highest- to lowest-order term without requiring any bit */ /* shuffling on our part. Reception works similarly. */ /* */ /* The feedback terms table consists of 256, 32-bit entries. Notes: */ /* */ /* The table can be generated at runtime if desired; code to do so */ /* is shown later. It might not be obvious, but the feedback */ /* terms simply represent the results of eight shift/xor opera- */ /* tions for all combinations of data and CRC register values. */ /* */ /* The values must be right-shifted by eight bits by the "updcrc" */ /* logic; the shift must be unsigned (bring in zeroes). On some */ /* hardware you could probably optimize the shift in assembler by */ /* using byte-swap instructions. */ /* polynomial $edb88320 */ /* */ /* -------------------------------------------------------------------- */ static unsigned long crc32_tab[] = { 0x00000000L, 0x77073096L, 0xee0e612cL, 0x990951baL, 0x076dc419L, 0x706af48fL, 0xe963a535L, 0x9e6495a3L, 0x0edb8832L, 0x79dcb8a4L, 0xe0d5e91eL, 0x97d2d988L, 0x09b64c2bL, 0x7eb17cbdL, 0xe7b82d07L, 0x90bf1d91L, 0x1db71064L, 0x6ab020f2L, 0xf3b97148L, 0x84be41deL, 0x1adad47dL, 0x6ddde4ebL, 0xf4d4b551L, 0x83d385c7L, 0x136c9856L, 0x646ba8c0L, 0xfd62f97aL, 0x8a65c9ecL, 0x14015c4fL, 0x63066cd9L, 0xfa0f3d63L, 0x8d080df5L, 0x3b6e20c8L, 0x4c69105eL, 0xd56041e4L, 0xa2677172L, 0x3c03e4d1L, 0x4b04d447L, 0xd20d85fdL, 0xa50ab56bL, 0x35b5a8faL, 0x42b2986cL, 0xdbbbc9d6L, 0xacbcf940L, 0x32d86ce3L, 0x45df5c75L, 0xdcd60dcfL, 0xabd13d59L, 0x26d930acL, 0x51de003aL, 0xc8d75180L, 0xbfd06116L, 0x21b4f4b5L, 0x56b3c423L, 0xcfba9599L, 0xb8bda50fL, 0x2802b89eL, 0x5f058808L, 0xc60cd9b2L, 0xb10be924L, 0x2f6f7c87L, 0x58684c11L, 0xc1611dabL, 0xb6662d3dL, 0x76dc4190L, 0x01db7106L, 0x98d220bcL, 0xefd5102aL, 0x71b18589L, 0x06b6b51fL, 0x9fbfe4a5L, 0xe8b8d433L, 0x7807c9a2L, 0x0f00f934L, 0x9609a88eL, 0xe10e9818L, 0x7f6a0dbbL, 0x086d3d2dL, 0x91646c97L, 0xe6635c01L, 0x6b6b51f4L, 0x1c6c6162L, 0x856530d8L, 0xf262004eL, 0x6c0695edL, 0x1b01a57bL, 0x8208f4c1L, 0xf50fc457L, 0x65b0d9c6L, 0x12b7e950L, 0x8bbeb8eaL, 0xfcb9887cL, 0x62dd1ddfL, 0x15da2d49L, 0x8cd37cf3L, 0xfbd44c65L, 0x4db26158L, 0x3ab551ceL, 0xa3bc0074L, 0xd4bb30e2L, 0x4adfa541L, 0x3dd895d7L, 0xa4d1c46dL, 0xd3d6f4fbL, 0x4369e96aL, 0x346ed9fcL, 0xad678846L, 0xda60b8d0L, 0x44042d73L, 0x33031de5L, 0xaa0a4c5fL, 0xdd0d7cc9L, 0x5005713cL, 0x270241aaL, 0xbe0b1010L, 0xc90c2086L, 0x5768b525L, 0x206f85b3L, 0xb966d409L, 0xce61e49fL, 0x5edef90eL, 0x29d9c998L, 0xb0d09822L, 0xc7d7a8b4L, 0x59b33d17L, 0x2eb40d81L, 0xb7bd5c3bL, 0xc0ba6cadL, 0xedb88320L, 0x9abfb3b6L, 0x03b6e20cL, 0x74b1d29aL, 0xead54739L, 0x9dd277afL, 0x04db2615L, 0x73dc1683L, 0xe3630b12L, 0x94643b84L, 0x0d6d6a3eL, 0x7a6a5aa8L, 0xe40ecf0bL, 0x9309ff9dL, 0x0a00ae27L, 0x7d079eb1L, 0xf00f9344L, 0x8708a3d2L, 0x1e01f268L, 0x6906c2feL, 0xf762575dL, 0x806567cbL, 0x196c3671L, 0x6e6b06e7L, 0xfed41b76L, 0x89d32be0L, 0x10da7a5aL, 0x67dd4accL, 0xf9b9df6fL, 0x8ebeeff9L, 0x17b7be43L, 0x60b08ed5L, 0xd6d6a3e8L, 0xa1d1937eL, 0x38d8c2c4L, 0x4fdff252L, 0xd1bb67f1L, 0xa6bc5767L, 0x3fb506ddL, 0x48b2364bL, 0xd80d2bdaL, 0xaf0a1b4cL, 0x36034af6L, 0x41047a60L, 0xdf60efc3L, 0xa867df55L, 0x316e8eefL, 0x4669be79L, 0xcb61b38cL, 0xbc66831aL, 0x256fd2a0L, 0x5268e236L, 0xcc0c7795L, 0xbb0b4703L, 0x220216b9L, 0x5505262fL, 0xc5ba3bbeL, 0xb2bd0b28L, 0x2bb45a92L, 0x5cb36a04L, 0xc2d7ffa7L, 0xb5d0cf31L, 0x2cd99e8bL, 0x5bdeae1dL, 0x9b64c2b0L, 0xec63f226L, 0x756aa39cL, 0x026d930aL, 0x9c0906a9L, 0xeb0e363fL, 0x72076785L, 0x05005713L, 0x95bf4a82L, 0xe2b87a14L, 0x7bb12baeL, 0x0cb61b38L, 0x92d28e9bL, 0xe5d5be0dL, 0x7cdcefb7L, 0x0bdbdf21L, 0x86d3d2d4L, 0xf1d4e242L, 0x68ddb3f8L, 0x1fda836eL, 0x81be16cdL, 0xf6b9265bL, 0x6fb077e1L, 0x18b74777L, 0x88085ae6L, 0xff0f6a70L, 0x66063bcaL, 0x11010b5cL, 0x8f659effL, 0xf862ae69L, 0x616bffd3L, 0x166ccf45L, 0xa00ae278L, 0xd70dd2eeL, 0x4e048354L, 0x3903b3c2L, 0xa7672661L, 0xd06016f7L, 0x4969474dL, 0x3e6e77dbL, 0xaed16a4aL, 0xd9d65adcL, 0x40df0b66L, 0x37d83bf0L, 0xa9bcae53L, 0xdebb9ec5L, 0x47b2cf7fL, 0x30b5ffe9L, 0xbdbdf21cL, 0xcabac28aL, 0x53b39330L, 0x24b4a3a6L, 0xbad03605L, 0xcdd70693L, 0x54de5729L, 0x23d967bfL, 0xb3667a2eL, 0xc4614ab8L, 0x5d681b02L, 0x2a6f2b94L, 0xb40bbe37L, 0xc30c8ea1L, 0x5a05df1bL, 0x2d02ef8dL }; // 根据输入的字符串计算一个 64 位的 CRC static unsigned long crc32(const uint8_t *s, unsigned int len) { unsigned int i; uint64_t crc32val; crc32val = 0LL; for (i = 0; i < len; i ++) { crc32val = crc32_tab[(crc32val ^ s[i]) & 0xff] ^ (crc32val >> 8); } return crc32val; }
我们的哈希表使用 knuth multiplicative 方法将字符串转为CRC,另一个可用的方法是 Murmur3,但是我也不清楚什么才是最佳的哈希算法。
列表
接下来我们会用到列表 list,虽然 vector 可以通过他的缓存友好性来提升一些性能,但是对于我们的需求来说也没有太大的收益。O(1)的数据插入复杂度对于我们来说完全足够使用了。我们的列表会基于一个单向链表,带有头部和尾部的指针,这样可以保证我们从两侧插入时的复杂度都为O(1)。
src/list.h// 节点 struct list_node { void *data; struct list_node *next; }; // 列表 typedef struct list { struct list_node *head; // 头指针 struct list_node *tail; // 尾指针 unsigned long len; int (*destructor)(struct list_node *); } List; // 比较函数接口, 用来比较两个节点 typedef int (*compare_func)(void *, void *); // 创建列表 List *list_create(int (*destructor)(struct list_node*)); // 释放链表, 通过一个 int 的标志来决定释放深度 // 例如:判断是否需要释放所有的节点中的数据 void list_release(List *, int); // 当前大小 unsigned long list_size(const List *); // 清空链表, 但保留链表本身, 根据 int 判断是否释放节点中的数据 void list_clear(List *, int); // 在头部插入数据 List *list_push(List *, void *); // 在尾部插入数据 List *list_push_back(List *, void *); // 通过传入的比较函数, 删除和第二参数相同的节点 void list_remove(List *, struct list_node *, compare_func); // 删除一个节点并返回被删除的节点 struct list_node *list_remove_node(List *, void *, compare_func); // 另一个比较函数接口, 用来进行合并或排序 typedef int cmp(void *, void *); // 再 cmp_func 计算的位置插入一个节点 struct list_node *list_sort_insert(struct list_node **, struct list_node *, compare_func); // 将 list 从中间分为两份 struct list_node *bisect_list(struct list_node *);
src/list.c#include "list.h" #include <stdlib.h> // 私有的删除节点函数 static struct list_node *list_node_remove(struct list_node *, struct list_node *, compare_func, int *); // 创建列表 List *list_create(int (*destructor)(struct list_node *)) { List *l = malloc(sizeof(List)); if (!l) return NULL; // 默认值 l->head = l->tail = NULL; l->len = 0L; // TODO 默认析构 l->destructor = destructor; return l; } // 释放列表 void list_release(List *l, int deep) { if (!l) return; struct list_node *h = l->head; struct list_node *tmp; // 释放所有节点 while (l->len--) { tmp = h->next; if (l->destructor) l->destructor(h); else { if (h) { // 如果需要释放数据 if (h->data && deep == 1) free(h->data); free(h); } } h = tmp; } // 释放列表本身 free(l); } unsigned long list_size(const List *list) { return list->len; } // 清空链表, 但保留链表本身, 根据 int 判断是否释放节点中的数据 void list_clear(List *l, int deep) { if (!l || !l->head) return; struct list_node *h = l->head; struct list_node *tmp; // 释放所有节点 while (l->len--) { tmp = h->next; if (h) { if (h->data && deep == 1) free(h->data); free(h); } h = tmp; } l->head = l->tail = NULL; l->len = 0L; } // 插入一个数据到头部 List *list_push(List *l, void *val) { struct list_node *new_node = malloc(sizeof(struct list_node)); if (!new_node) return NULL; new_node->data = val; // 第一个数据即使头也是尾 if (l->len == 0) { l->head = l->tail = new_node; new_node->next = NULL; // 插入为头部 } else { new_node->next = l->head; l->head = new_node; } l->len++; return l; } // 插入一个数据到尾部 List *list_push_back(List *l, void *val) { struct list_node *new_node = malloc(sizeof(struct list_node)); if (!new_node) return NULL; new_node->data = val; new_node->next = NULL; if (l->len == 0) { l->head = l->tail = new_node; } else { l->tail->next = new_node; l->tail = new_node; } l->len++; return l; } // 通过传入的比较函数, 删除一个节点 void list_remove(List *l, struct list_node *node, compare_func cmp) { if (!l || !node) return; int counter = 0; // list_node_remove 会递归的一层一层返回下一个节点指针, 并在其中去除被删除的节点 l->head = list_node_remove(l->head, node, cmp, &counter); l->len -= counter; } // 删除节点的工具方法 // return 递归用的返回, 删除成功后的那次调用会返回被删除节点的 next // head 传入遍历起点 // node 需要删除的节点的样子 // cmp 比较函数, 用来比较遍历的节点和传入的node // counter 被删除节点的数量, 0 或者 1 static struct list_node *list_node_remove(struct list_node *head, struct list_node *node, compare_func cmp, int *counter) { if (!head) return NULL; if (cmp(head, node) == 0) { struct list_node *tmp_next = head->next; // 译者认为这里没有考虑节点的data也可能需要释放, 或者是作者觉得可以在cmp中释放? free(head); head = NULL; // 匹配成功就 return 的话,这里实际只能删除第一个匹配的节点 (*counter)++; return tmp_next; } head->next = list_node_remove(head->next, node, cmp, counter); return head; } // 删除一个节点的工具方法 // return 递归的返回 // head 查询起点 // data 被删除的 node 的形状 // ret 返回被删除的 node // cmp 比较函数 static struct list_node *list_remove_single_node(struct list_node *head, void *data, struct list_node **ret, compare_func cmp) { if (!head) return NULL; if (cmp(head, data) == 0 && !*ret) { struct list_node *tmp_next = head->next; *ret = head; return tmp_next; } head->next = list_remove_single_node(head->next, data, ret, cmp); return head; } // 删除一个节点并返回被删除的节点 struct list_node *list_remove_node(List *list, void *data, compare_func cmp) { if (list->len == 0 || !list) return NULL; struct list_node *node = NULL; list_remove_single_node(list->head, data, &node, cmp); if (node) { list->len--; node->next = NULL; } return node; } // 在 cmp_func 计算的位置插入一个节点 struct list_node *list_sort_insert(struct list_node **head, struct list_node *new, cmp cmp_func) { if (!*head || cmp_func(*head, new) >= 0) { new->next = *head; *head = new; } else { struct list_node *cur; cur = *head; while (cur->next && cmp_func(cur->next, new) < 0) cur = cur->next; new->next = cur->next; cur->next = new; } return *head; } // 返回一个靠近中间的 node, 并且已经将原 list 从此处截断 struct list_node *bisect_list(struct list_node *head) { // fast 的移动速度是 slow 的两倍 // prev 表示 slow的前一个节点, 也就是截取后的第一个 list 的最后一个节点 struct list_node *fast = head, *slow = head, *prev = NULL; while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) { fast = fast->next->next; prev = slow; slow = slow->next; } if (prev != NULL) prev->next = NULL; return slow; }
结尾
我们成功的实现了两个经典的数据结构,这样我们可以在项目中使用他们:
- 哈希表
- 列表
下一个要实现的数据结构是 特里树,他可以让我们轻松的维护我们的主题和主题的分层结构。