[翻译]Sol - 从零开始的MQTT broker - 第六部分:处理器
这一部分我们会重点关注 处理器(handler) 的实现,每种处理器用来处理一种对应的MQTT包。就像我们在第四部分中已经描述的,我们把处理器放在一个固定长度的数组里,每个处理器的索引恰好是包的MQTT类型。
业务封装
在我们开始主要工作之前,我们先补充一些前几章缺失的业务代码:
src/core.h#include "trie.h" #include "list.h" #include "hashtable.h" struct topic { const char *name; List *subscribers; }; // sol的主体结构, 服务器运行时会产生一个全局实例 // 包括了所有连接的客户端、闭包和主题树 struct sol { HashTable *clients; HashTable *closures; Trie topics; }; // 在客户端中使用的session, 保存该客户端订阅的所有主题 struct session { List *subscriptions; // TODO add pending confirmed messages }; // 客户端包装 struct sol_client { char *client_id; int fd; struct session session; }; // 将客户端包装成订阅者, 之后由主题保存订阅者列表 struct subscriber { unsigned qos; struct sol_client *client; }; // 主题创建、订阅发布的一系列方法 struct topic *topic_create(const char *); void topic_init(struct topic *, const char *); void topic_add_subscriber(struct topic *, struct sol_client *, unsigned, bool); void topic_del_subscriber(struct topic *, struct sol_client *, bool); void sol_topic_put(struct sol *, struct topic *); void sol_topic_del(struct sol *, const char *); // 通过主题名称获得主题 struct topic *sol_topic_get(struct sol *, const char *);
这部分主要实现了客户端和服务端交互的各种抽象:
- 客户端(client)结构体,用来表示已经建立连接的客户端
- 主题(topic)结构体
- 订阅者(subscriber)结构体
- 会话结(session)构体,表示客户端持有的会话,仅当
clean session选项为false时生效 - sol结构体,全局运行实例,用来持有上述的所有内容
- 一些方便的辅助函数
这里是上述定义的实现:
src/core.c#include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "core.h" // 传入两个订阅者, 比较其客户端id static int compare_cid(void *c1, void *c2) { return strcmp(((struct subscriber *) c1)->client->client_id, ((struct subscriber *) c2)->client->client_id); } // 创建一个topic对象 struct topic *topic_create(const char *name) { struct topic *t = malloc(sizeof(*t)); topic_init(t, name); return t; } void topic_init(struct topic *t, const char *name) { t->name = name; t->subscribers = list_create(NULL); } // 向主题对象内添加一个订阅者 void topic_add_subscriber(struct topic *t, struct sol_client *client, unsigned qos, bool cleansession) { struct subscriber *sub = malloc(sizeof(*sub)); sub->client = client; sub->qos = qos; t->subscribers = list_push(t->subscribers, sub); // 如果cleansession置为false,必须将此订阅加入会话 if (!cleansession) client->session.subscriptions = list_push(client->session.subscriptions, t); } // 主题取消客户端订阅 void topic_del_subscriber(struct topic *t, struct sol_client *client, bool cleansession) { list_remove_node(t->subscribers, client, compare_cid); // TODO remomve in case of cleansession == false } // 向sol设置主题 void sol_topic_put(struct sol *sol, struct topic *t) { trie_insert(&sol->topics, t->name, t); } // 向sol删除主题 void sol_topic_del(struct sol *sol, const char *name) { trie_delete(&sol->topics, name); } // 查询获得一个主题 struct topic *sol_topic_get(struct sol *sol, const char *name) { struct topic *ret_topic; trie_find(&sol->topics, name, (void *) &ret_topic); return ret_topic; }
处理器实现
处理器(Handlers) 是一系列会在 on_read 中被执行的回调函数,就像他们的名称暗示的一样,他们负责处理客户端输入的数据,之后他们选择性的创建或不创建一个回复数据,并且返回一个指示下一步应该如何处理的返回值。返回值可以是:
REARM_W,表示将下一个触发函数设置为on_write,并提供需要发送到客户端的数据REARM_R,表示没有需要回复客户端的数据,可以继续将触发函数重置为on_read,继续等待客户端数据-REARM_W,这个状态码没有被协议定义,我们在这里用来表示客户端断开链接或者故障发生
CONNECT 处理器
按照顺序,我们先来实现 connect_handler,顾名思义,他用来处理客户端完成TCP链接之后发来的第一个数据包,也就是 CONNECT 包。
src/server.cstatic int connect_handler(struct closure *cb, union mqtt_packet *pkt) { // 当一个已存在的客户端又发送了 CONNECT 包, 被视为违背协议 // 因此断开链接 if (hashtable_exists(sol.clients, (const char *) pkt->connect.payload.client_id)) { sol_info("Received double CONNECT from %s, disconnecting client", pkt->connect.payload.client_id); // 关闭链接, 释放资源 close(cb->fd); // 哈希表删除时的回调会负责销毁 client 或者 cb hashtable_del(sol.clients, (const char *) pkt->connect.payload.client_id); hashtable_del(sol.closures, cb->closure_id); // 更新状态 info.nclients--; info.nconnections--; return -REARM_W; } sol_info("New client connected as %s (c%i, k%u)", pkt->connect.payload.client_id, pkt->connect.bits.clean_session, pkt->connect.payload.keepalive); // 添加新链接 struct sol_client *new_client = malloc(sizeof(*new_client)); new_client->fd = cb->fd; // 由客户端保证cid的唯一性, 比如可以用mac地址 const char *cid = (const char *) pkt->connect.payload.client_id; new_client->client_id = strdup(cid); hashtable_put(sol.clients, cid, new_client); // 将 clinet 绑定到闭包 cb->obj = new_client; // 使用 CONNACK回复 union mqtt_packet *response = malloc(sizeof(*response)); // 高位赋值 unsigned char byte = CONNACK_BYTE; // clean_session == false 表示此链接支持保存 session if (pkt->connect.bits.clean_session == false) // 所以需要在会话中初始化订阅列表 new_client->session.subscriptions = list_create(NULL); // TODO 处理确实存在session的情况 // 这里暂时是简单的返回 session 不存在 unsigned char session_present = 0; unsigned char connect_flags = 0 | (session_present & 0x1) << 0; unsigned char rc = 0; // 返回 0 表示接收链接 // 完成组包 response->connack = *mqtt_packet_connack(byte, connect_flags, rc); // 包编码成数据流 cb->payload = bytestring_create(MQTT_ACK_LEN); unsigned char *p = pack_mqtt_packet(response, CONNACK); memcpy(cb->payload->data, p, MQTT_ACK_LEN); free(p); sol_debug("Sending CONNACK to %s (%u, %u)", pkt->connect.payload.client_id, session_present, rc); free(response); // 标记之后发送 return REARM_W; }
我们严格按照协议规范实现了处理器行为,除了 clean session 标识的处理,对于有会话的客户端该如何重连这件事我们暂时忽略了。如果一个客户端传入了两次 CONNECT,按照协议规范我们会断开他的链接。正常情况下我们会记录客户端,制作一个 CONNACK 数据流,并且返回 REARM_W,让 on_write 可以把我们的数据流发送回客户端。
DISCONNECT 处理器
下一个包,DISCONNECT:
src/server.cstatic int disconnect_handler(struct closure *cb, union mqtt_packet *pkt) { // 获得客户端 struct sol_client *c = cb->obj; // 执行删除动作 sol_debug("Received DISCONNECT from %s", c->client_id); close(c->fd); hashtable_del(sol.clients, c->client_id); hashtable_del(sol.closures, cb->closure_id); // 跟新状态 info.nclients--; info.nconnections--; // TODO 在该客户端订阅的所有主题中删除对其的引用 return -REARM_W; }
我们做了最简单的处理:日志记录、关闭 fd、从哈希表中删除、更新信息,然后返回一个负值。
SUBSCRIBE UNSUBSCRIBE 处理器
SUBSCRIBE 的处理器则是一个更加有意思的操作,在这里我们需要用到我们的 特里树,大概流程如下:
- 迭代传入的主题元组(包括 tpoic,QoS),对每一个主题进行如下操作:
- 如果主题不存在,我们创建该主题
- 将客户端加入该主题的订阅者列表
- 如果主题以
#结尾,我们需要让客户端订阅该主题以及该主题所有的下级节点,由于特里树的数据结构设计,这个操作可以轻松的递归处理 - 如果
clean_session标识的值为false,我们需要给客户端添加一个会话,这里我们还没有完全实现
- 使用
SUBACK回应
在 UNSUBSCRIBE 中也没有什么意外,只要在主题中删除客户端,然后使用 UNSUBACK 回应即可。
src/server.c// 用递归方式来订阅一个节点所有子节点的辅助函数 static void recursive_subscription(struct trie_node *node, void *arg) { if (!node || !node->data) return; struct list_node *child = node->children->head; for (; child; child = child->next) recursive_subscription(child->data, arg); struct topic *t = node->data; struct subscriber *s = arg; t->subscribers = list_push(t->subscribers, s); } // SUBSCRIBE 处理器 static int subscribe_handler(struct closure *cb, union mqtt_packet *pkt) { struct sol_client *c = cb->obj; bool wildcard = false; // 标记是否通配 bool alloced = false; // 表示有新 malloc 的string, 用完需要释放 // 在 SUBACK 中使用和 SUB 同样的主题顺序回复的 QoS List unsigned char rcs[pkt->subscribe.tuples_len]; // SUBSCRIBE 包含了主题和QoS的列表, 此处循环处理 for (unsigned i = 0; i < pkt->subscribe.tuples_len; i++) { sol_debug("Received SUBSCRIBE from %s", c->client_id); // 获得单个元组的主题字符串和QoS char *topic = (char *) pkt->subscribe.tuples[i].topic; sol_debug("\t%s (QoS %i)", topic, pkt->subscribe.tuples[i].qos); // 当使用 /# 结尾时, 标记通配 if (topic[pkt->subscribe.tuples[i].topic_len - 1] == '#' && topic[pkt->subscribe.tuples[i].topic_len - 2] == '/') { topic = remove_occur(topic, '#'); wildcard = true; } else if (topic[pkt->subscribe.tuples[i].topic_len - 1] != '/') { // 如果不以 / 结尾, 添加 / topic = append_string((char *) pkt->subscribe.tuples[i].topic, "/", 1); alloced = true; } // 通过 topic 字符串找到对象 struct topic *t = sol_topic_get(&sol, topic); // 当没有找到对象时, 创建并添加到特里树 if (!t) { t = topic_create(strdup(topic)); sol_topic_put(&sol, t); } else if (wildcard == true) { struct subscriber *sub = malloc(sizeof(*sub)); sub->client = cb->obj; sub->qos = pkt->subscribe.tuples[i].qos; // 让该节点和所有子节点都拥有表示此客户端的 subscriber trie_prefix_map_tuple(&sol.topics, topic, recursive_subscription, sub); } // 暂时都使用 cleansession = true // 译者觉得在通配符的情况下这里会到这 topic 对应的节点产生两个 subscriber topic_add_subscriber(t, cb->obj, pkt->subscribe.tuples[i].qos, true); if (alloced) free(topic); rcs[i] = pkt->subscribe.tuples[i].qos; } // 制作 suback struct mqtt_suback *suback = mqtt_packet_suback(SUBACK_BYTE, pkt->subscribe.pkt_id, rcs, pkt->subscribe.tuples_len); // 复用pkt mqtt_packet_release(pkt, SUBSCRIBE); pkt->suback = *suback; // 制作数据流并发出 unsigned char *packed = pack_mqtt_packet(pkt, SUBACK); size_t len = MQTT_HEADER_LEN + sizeof(uint16_t) + pkt->subscribe.tuples_len; cb->payload = bytestring_create(len); memcpy(cb->payload->data, packed, len); free(packed); mqtt_packet_release(pkt, SUBACK); free(suback); sol_debug("Sending SUBACK to %s", c->client_id); return REARM_W; } // UNSUBSCRIBE 处理器 这里没做实际处理, 只是正确回复ACK static int unsubscribe_handler(struct closure *cb, union mqtt_packet *pkt) { struct sol_client *c = cb->obj; sol_debug("Received UNSUBSCRIBE from %s", c->client_id); pkt->ack = *mqtt_packet_ack(UNSUBACK_BYTE, pkt->unsubscribe.pkt_id); unsigned char *packed = pack_mqtt_packet(pkt, UNSUBACK); cb->payload = bytestring_create(MQTT_ACK_LEN); memcpy(cb->payload->data, packed, MQTT_ACK_LEN); free(packed); sol_debug("Sending UNSUBACK to %s", c->client_id); return REARM_W; }
PUBLISH 处理器
PUBLISH 处理器会比我们前面写的几个内容多一些,但是十分好理解:
- 如果发布的主题不存在, 则创建
- 基于消息的 QoS 设置,使用正确的 ACK 回复:
- QoS0:至多一次,不回复
- QoS1:至少一次,使用 PUBACK 回复
- QoS2:确保一次,使用 PUBREC 回复
- 向该主题的订阅者转发该消息,转发的 QoS 值应该是由消息的 QoS 决定,但不能大于接收方设置的最大 QoS 值
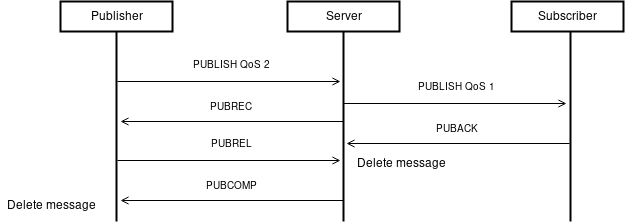
src/server.c// PUBLISH 处理器 static int publish_handler(struct closure *cb, union mqtt_packet *pkt) { struct sol_client *c = cb->obj; sol_debug("Received PUBLISH from %s (d%i, q%u, r%i, m%u, %s, ... (%i bytes))", c->client_id, pkt->publish.header.bits.dup, pkt->publish.header.bits.qos, pkt->publish.header.bits.retain, pkt->publish.pkt_id, pkt->publish.topic, pkt->publish.payloadlen); // 数据记录 info.messages_recv++; char *topic = (char *) pkt->publish.topic; bool alloced = false; // 标记字符串空间是分配的 unsigned char qos = pkt->publish.header.bits.qos; // 保证所有的主题都是用 / 结尾 if (topic[pkt->publish.topiclen - 1] != '/') { topic = append_string((char *) pkt->publish.topic, "/", 1); alloced = true; } // 获得或创建基于该 kye 的 topic 对象 struct topic *t = sol_topic_get(&sol, topic); if (!t) { t = topic_create(strdup(topic)); sol_topic_put(&sol, t); } if (alloced == true) free(topic); size_t publen; unsigned char *pub; struct list_node *cur = t->subscribers->head; for (; cur; cur = cur->next) { publen = MQTT_HEADER_LEN + sizeof(uint16_t) + pkt->publish.topiclen + pkt->publish.payloadlen; struct subscriber *sub = cur->data; struct sol_client *sc = sub->client; // 将 QoS 设置为订阅者的 QoS (此处为方便设计,并未完全遵循协议) pkt->publish.header.bits.qos = sub->qos; if (pkt->publish.header.bits.qos > AT_MOST_ONCE) publen += sizeof(uint16_t); int remaininglen_offset = 0; if ((publen - 1) > 0x200000) remaininglen_offset = 3; else if ((publen - 1) > 0x4000) remaininglen_offset = 2; else if ((publen - 1) > 0x80) remaininglen_offset = 1; publen += remaininglen_offset; // 发送给该订阅者的 PUB 包 pub = pack_mqtt_packet(pkt, PUBLISH); ssize_t sent; if ((sent = send_bytes(sc->fd, pub, publen)) < 0) sol_error("Error publishing to %s: %s", sc->client_id, strerror(errno)); // 记录信息 info.bytes_sent += sent; sol_debug("Sending PUBLISH to %s (d%i, q%u, r%i, m%u, %s, ... (%i bytes))", sc->client_id, pkt->publish.header.bits.dup, pkt->publish.header.bits.qos, pkt->publish.header.bits.retain, pkt->publish.pkt_id, pkt->publish.topic, pkt->publish.payloadlen); info.messages_sent++; free(pub); } // 至少一次 使用ACK回复 if (qos == AT_LEAST_ONCE) { mqtt_puback *puback = mqtt_packet_ack(PUBACK_BYTE, pkt->publish.pkt_id); mqtt_packet_release(pkt, PUBLISH); pkt->ack = *puback; unsigned char *packed = pack_mqtt_packet(pkt, PUBACK); cb->payload = bytestring_create(MQTT_ACK_LEN); memcpy(cb->payload->data, packed, MQTT_ACK_LEN); free(packed); sol_debug("Sending PUBACK to %s", c->client_id); return REARM_W; } else if (qos == EXACTLY_ONCE) { // 确保一次 使用 PUBREC 回复 // TODO 需要通过一个哈希表记录已经处于 PUBREC 状态的客户端+包id mqtt_pubrec *pubrec = mqtt_packet_ack(PUBREC_BYTE, pkt->publish.pkt_id); mqtt_packet_release(pkt, PUBLISH); pkt->ack = *pubrec; unsigned char *packed = pack_mqtt_packet(pkt, PUBREC); cb->payload = bytestring_create(MQTT_ACK_LEN); memcpy(cb->payload->data, packed, MQTT_ACK_LEN); free(packed); sol_debug("Sending PUBREC to %s", c->client_id); return REARM_W; } // 至多一次 无需回复 mqtt_packet_release(pkt, PUBLISH); return REARM_R; }
ACK PINGREQ 处理器
只剩下 ACK 处理器了,他们基本上都是一样的。现在我们只做基本的日志和回复,以后我们再来实现基于 QoS 的业务机制。
还有 PINGREQ 处理器,这是客户端用来确认链接状态的心跳报文,我们只需要用 PINGRESP 回复即可。
src/server.c// PUBACK 处理器 static int puback_handler(struct closure *cb, union mqtt_packet *pkt) { sol_debug("Received PUBACK from %s", ((struct sol_client *) cb->obj)->client_id); // TODO 基于QoS机制, 将该数据移出需重传列表 return REARM_R; } // PUBREC 处理器 static int pubrec_handler(struct closure *cb, union mqtt_packet *pkt) { struct sol_client *c = cb->obj; sol_debug("Received PUBREC from %s", c->client_id); // 按照协议使用 RELEASE 回复 RECIVE mqtt_pubrel *pubrel = mqtt_packet_ack(PUBREL_BYTE, pkt->publish.pkt_id); pkt->ack = *pubrel; unsigned char *packed = pack_mqtt_packet(pkt, PUBREC); cb->payload = bytestring_create(MQTT_ACK_LEN); memcpy(cb->payload->data, packed, MQTT_ACK_LEN); free(packed); sol_debug("Sending PUBREL to %s", c->client_id); return REARM_W; } // PUBREL 处理器 static int pubrel_handler(struct closure *cb, union mqtt_packet *pkt) { sol_debug("Received PUBREL from %s", ((struct sol_client *) cb->obj)->client_id); // 按照协议使用 COMPLETE 回复 RELEASE mqtt_pubcomp *pubcomp = mqtt_packet_ack(PUBCOMP_BYTE, pkt->publish.pkt_id); pkt->ack = *pubcomp; unsigned char *packed = pack_mqtt_packet(pkt, PUBCOMP); cb->payload = bytestring_create(MQTT_ACK_LEN); memcpy(cb->payload->data, packed, MQTT_ACK_LEN); free(packed); sol_debug("Sending PUBCOMP to %s", ((struct sol_client *) cb->obj)->client_id); return REARM_W; } // PUBCOMP 处理器 static int pubcomp_handler(struct closure *cb, union mqtt_packet *pkt) { sol_debug("Received PUBCOMP from %s", ((struct sol_client *) cb->obj)->client_id); // TODO 基于 QoS 机制将其从待确认列表移出 return REARM_R; } // PINGREQ 处理器 static int pingreq_handler(struct closure *cb, union mqtt_packet *pkt) { sol_debug("Received PINGREQ from %s", ((struct sol_client *) cb->obj)->client_id); // 按照协议使用 PINGRESP 回复 pkt->header = *mqtt_packet_header(PINGRESP_BYTE); unsigned char *packed = pack_mqtt_packet(pkt, PINGRESP); cb->payload = bytestring_create(MQTT_HEADER_LEN); memcpy(cb->payload->data, packed, MQTT_HEADER_LEN); free(packed); sol_debug("Sending PINGRESP to %s", ((struct sol_client *) cb->obj)->client_id); return REARM_W; }
现在我们的 broker 已经具有基本的功能,很快就可以和其他的 MQTT 工具联调测试,例如使用 mosquitto_sub 和 mosquitto_pub 或 Python 中的 paho-mqtt。
配置模块
配置文件
我们需要一个配置模块来设置各种参数,使用最经典的键值对的方式:
conf/sol.conf# Sol configuration file, uncomment and edit desired configuration # Network configuration # Uncomment ip_address and ip_port to set socket family to TCP, if unix_socket # is set, UNIX family socket will be used # ip_address 127.0.0.1 # ip_port 9090 unix_socket /tmp/sol.sock # Logging configuration # Could be either DEBUG, INFO/INFORMATION, WARNING, ERROR log_level DEBUG log_path /tmp/sol.log # Max memory to be used, after which the system starts to reclaim memory by # freeing older items stored max_memory 2GB # Max memory that will be allocated for each request max_request_size 50MB # TCP backlog, size of the complete connection queue tcp_backlog 128 # Interval of time between one stats publish on $SOL topics and the subsequent stats_publish_interval 10s
配置模块定义
src/config.h#include <stdio.h> // 默认参数 #define VERSION "0.0.1" #define DEFAULT_SOCKET_FAMILY INET #define DEFAULT_LOG_LEVEL DEBUG #define DEFAULT_LOG_PATH "/tmp/sol.log" #define DEFAULT_CONF_PATH "/etc/sol/sol.conf" #define DEFAULT_HOSTNAME "127.0.0.1" #define DEFAULT_PORT "1883" #define DEFAULT_MAX_MEMORY "2GB" #define DEFAULT_MAX_REQUEST_SIZE "2MB" #define DEFAULT_STATS_INTERVAL "10s" struct config { /* Sol version <MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH> */ const char *version; /* Eventfd to break the epoll_wait loop in case of signals */ int run; /* Logging level, to be set by reading configuration */ int loglevel; /* Epoll wait timeout, define even the number of times per second that the system will check for expired keys */ int epoll_timeout; /* Socket family (Unix domain or TCP) */ int socket_family; /* Log file path */ char logpath[0xFF]; /* Hostname to listen on */ char hostname[0xFF]; /* Port to open while listening, only if socket_family is INET, * otherwise it's ignored */ char port[0xFF]; /* Max memory to be used, after which the system starts to reclaim back by * freeing older items stored */ size_t max_memory; /* Max memory request can allocate */ size_t max_request_size; /* TCP backlog size */ int tcp_backlog; /* Delay between every automatic publish of broker stats on topic */ size_t stats_pub_interval; }; // 全局配置对象 extern struct config *conf; void config_set_default(void); void config_print(void); int config_load(const char *); char *time_to_string(size_t); char *memory_to_string(size_t);
配置项目无需过多解释,都可以通过名称了解其作用。
配置模块实现
配置项主要是使用工具将配置文件的字符串信息解析成配置对象的值:
src/config.c#include <ctype.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <assert.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <sys/eventfd.h> #include "util.h" #include "config.h" #include "network.h" // 全局对象 static struct config config; struct config *conf; struct llevel { const char *lname; int loglevel; }; static const struct llevel lmap[5] = { {"DEBUG", DEBUG}, {"WARNING", WARNING}, {"ERROR", ERROR}, {"INFO", INFORMATION}, {"INFORMATION", INFORMATION} }; // 解析带单位的内存配置 static size_t read_memory_with_mul(const char *memory_string) { // 解析数字部分 size_t num = parse_int(memory_string); int mul = 1; // 指针指向单位 while (isdigit(*memory_string)) memory_string++; // 通过单位获得乘系数 if (STREQ(memory_string, "kb", 2)) mul = 1024; else if (STREQ(memory_string, "mb", 2)) mul = 1024 * 1024; else if (STREQ(memory_string, "gb", 2)) mul = 1024 * 1024 * 1024; return num * mul; } // 解析带单位的时间配置(默认秒) static size_t read_time_with_mul(const char *time_string) { size_t num = parse_int(time_string); int mul = 1; while (isdigit(*time_string)) time_string++; switch (*time_string) { case 'm': mul = 60; break; case 'd': mul = 60 * 60 * 24; break; default: mul = 1; break; } return num * mul; } // 将内存数字转为人类易读的字符串 例如 1024 => 1Kb char *memory_to_string(size_t memory) { int numlen = 0; int translated_memory = 0; char *mstring = NULL; if (memory < 1024) { translated_memory = memory; numlen = number_len(translated_memory); // 数字 + 'b' mstring = malloc(numlen + 1); snprintf(mstring, numlen + 1, "%db", translated_memory); } else if (memory < 1048576) { translated_memory = memory / 1024; numlen = number_len(translated_memory); // + "Kb" mstring = malloc(numlen + 2); snprintf(mstring, numlen + 2, "%dKb", translated_memory); } else if (memory < 1073741824) { translated_memory = memory / (1024 * 1024); numlen = number_len(translated_memory); // + "Mb" mstring = malloc(numlen + 2); snprintf(mstring, numlen + 2, "%dMb", translated_memory); } else { translated_memory = memory / (1024 * 1024 * 1024); numlen = number_len(translated_memory); // + "Gb" mstring = malloc(numlen + 2); snprintf(mstring, numlen + 2, "%dGb", translated_memory); } return mstring; } // 将时间数字转为人类易读的字符串 char *time_to_string(size_t time) { int numlen = 0; int translated_time = 0; char *tstring = NULL; if (time < 60) { translated_time = time; numlen = number_len(translated_time); tstring = malloc(numlen + 1); snprintf(tstring, numlen + 1, "%ds", translated_time); } else if (time < 60 * 60) { translated_time = time / 60; numlen = number_len(translated_time); tstring = malloc(numlen + 1); snprintf(tstring, numlen + 1, "%dm", translated_time); } else if (time < 60 * 60 * 24) { translated_time = time / (60 * 60); numlen = number_len(translated_time); tstring = malloc(numlen + 1); snprintf(tstring, numlen + 1, "%dh", translated_time); } else { translated_time = time / (60 * 60 * 24); numlen = number_len(translated_time); tstring = malloc(numlen + 1); snprintf(tstring, numlen + 1, "%dd", translated_time); } return tstring; } // 基于读取的 kv, 向配置对象赋值 static void add_config_value(const char *key, const char *value) { size_t klen = strlen(key); size_t vlen = strlen(value); if (STREQ("log_level", key, klen) == true) { for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { if (STREQ(lmap[i].lname, value, vlen) == true) config.loglevel = lmap[i].loglevel; } } else if (STREQ("log_path", key, klen) == true) { strcpy(config.logpath, value); } else if (STREQ("unix_socket", key, klen) == true) { config.socket_family = UNIX; strcpy(config.hostname, value); } else if (STREQ("ip_address", key, klen) == true) { config.socket_family = INET; strcpy(config.hostname, value); } else if (STREQ("ip_port", key, klen) == true) { strcpy(config.port, value); } else if (STREQ("max_memory", key, klen) == true) { config.max_memory = read_memory_with_mul(value); } else if (STREQ("max_request_size", key, klen) == true) { config.max_request_size = read_memory_with_mul(value); } else if (STREQ("tcp_backlog", key, klen) == true) { int tcp_backlog = parse_int(value); config.tcp_backlog = tcp_backlog <= SOMAXCONN ? tcp_backlog : SOMAXCONN; } else if (STREQ("stats_publish_interval", key, klen) == true) { config.stats_pub_interval = read_time_with_mul(value); } } // 去空格 static inline void strip_spaces(char **str) { if (!*str) return; while (isspace(**str) && **str) ++(*str); } static inline void unpack_bytes(char **str, char *dest) { if (!str || !dest) return; while (!isspace(**str) && **str) *dest++ = *(*str)++; } // 读取配置 int config_load(const char *configpath) { assert(configpath); FILE *fh = fopen(configpath, "r"); if (!fh) { sol_warning("WARNING: Unable to open conf file %s", configpath); sol_warning("To specify a config file run sol -c /path/to/conf"); return false; } char line[0xff], key[0xff], value[0xff]; int linenr = 0; char *pline, *pkey, *pval; while (fgets(line, 0xff, fh) != NULL) { memset(key, 0x00, 0xff); memset(value, 0x00, 0xff); linenr++; // 跳过注解 if (line[0] == '#') continue; // 删除key前的空格 pline = line; strip_spaces(&pline); if (*pline == '\0') continue; // key pkey = key; unpack_bytes(&pline, pkey); // 删除 key 后空格 strip_spaces(&pline); // 忽略错误的配置格式并提示 if (line[0] == '\0') { sol_warning("WARNING: Incomplete configuration '%s' at line %d. " "Fallback to default.", key, linenr); continue; } // 获得值 pval = value; unpack_bytes(&pline, pval); // 赋值 add_config_value(key, value); } return true; } // 设置默认参数 void config_set_default(void) { // 全局配置对象指针 conf = &config; // 默认赋值 config.version = VERSION; config.socket_family = DEFAULT_SOCKET_FAMILY; config.loglevel = DEFAULT_LOG_LEVEL; strcpy(config.logpath, DEFAULT_LOG_PATH); strcpy(config.hostname, DEFAULT_HOSTNAME); strcpy(config.port, DEFAULT_PORT); config.epoll_timeout = -1; config.run = eventfd(0, EFD_NONBLOCK); config.max_memory = read_memory_with_mul(DEFAULT_MAX_MEMORY); config.max_request_size = read_memory_with_mul(DEFAULT_MAX_REQUEST_SIZE); config.tcp_backlog = SOMAXCONN; config.stats_pub_interval = read_time_with_mul(DEFAULT_STATS_INTERVAL); } // 配置输出 void config_print(void) { if (config.loglevel < WARNING) { const char *sfamily = config.socket_family == UNIX ? "Unix" : "Tcp"; const char *llevel = NULL; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { if (lmap[i].loglevel == config.loglevel) llevel = lmap[i].lname; } sol_info("Sol v%s is starting", VERSION); sol_info("Network settings:"); sol_info("\tSocket family: %s", sfamily); if (config.socket_family == UNIX) { sol_info("\tUnix socket: %s", config.hostname); } else { sol_info("\tAddress: %s", config.hostname); sol_info("\tPort: %s", config.port); sol_info("\tTcp backlog: %d", config.tcp_backlog); } const char *human_rsize = memory_to_string(config.max_request_size); sol_info("\tMax request size: %s", human_rsize); sol_info("Logging:"); sol_info("\tlevel: %s", llevel); sol_info("\tlogpath: %s", config.logpath); const char *human_memory = memory_to_string(config.max_memory); sol_info("Max memory: %s", human_memory); free((char *) human_memory); free((char *) human_rsize); } }
主函数
最后的最后,main 函数:
src/sol.c#define _POSIX_C_SOURCE 2 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include "util.h" #include "config.h" #include "server.h" int main (int argc, char **argv) { char *addr = DEFAULT_HOSTNAME; char *port = DEFAULT_PORT; char *confpath = DEFAULT_CONF_PATH; int debug = 0; int opt; // 使用默认值赋值 config_set_default(); // 处理运行参数 while ((opt = getopt(argc, argv, "a:c:p:m:vn:")) != -1) { switch (opt) { case 'a': addr = optarg; strcpy(conf->hostname, addr); break; case 'c': confpath = optarg; break; case 'p': port = optarg; strcpy(conf->port, port); break; case 'v': debug = 1; break; default: fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s [-a addr] [-p port] [-c conf] [-v]\n", argv[0]); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } } // 通过参数设置 debug 等级 conf->loglevel = debug == 1 ? DEBUG : WARNING; // 读配置 config_load(confpath); sol_log_init(conf->logpath); // 打印配置 config_print(); // 运行服务 start_server(conf->hostname, conf->port); sol_log_close(); return 0; }
构建与运行
我们的 sol 项目运行的所有所需内容都完成了:
sol/
├── src/
│ ├── mqtt.h
│ ├── mqtt.c
│ ├── network.h
│ ├── network.c
│ ├── list.h
│ ├── list.c
│ ├── hashtable.h
│ ├── hashtable.c
│ ├── server.h
│ ├── server.c
│ ├── trie.h
│ ├── trie.c
│ ├── util.h
│ ├── util.c
│ ├── core.h
│ ├── core.c
│ ├── config.h
│ ├── config.c
│ ├── pack.h
│ ├── pack.c
│ └── sol.c
├── conf
│ └── sol.conf
├── CHANGELOG
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── COPYING
└── README.mdsol 项目的代码量并不算大,一般这种情况下我会编写 Makefile 用来控制编译。但是这一次,就像上方文件结构中描述的那样,我打算使用 CMakeLists.txt 来控制项目的构建:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(sol)
OPTION(DEBUG "add debug flags" OFF)
if (DEBUG)
message(STATUS "Configuring build for debug")
set(CMAKE_C_FLAGS "${CMAKE_C_FLAGS} -Wall -Wunused -Werror -std=c11 -O3 -pedantic -luuid -ggdb -fsanitize=address -fsanitize=undefined -fno-omit-frame-pointer -pg")
else (DEBUG)
message(STATUS "Configuring build for production")
set(CMAKE_C_FLAGS "${CMAKE_C_FLAGS} -Wall -Wunused -Werror -Wextra -std=c11 -O3 -pedantic -luuid")
endif (DEBUG)
set(EXECUTABLE_OUTPUT_PATH ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR})
file(GLOB SOURCES src/*.c)
set(AUTHOR "Andrea Giacomo Baldan")
set(LICENSE "BSD2 license")
# Executable
add_executable(sol ${SOURCES})唯一值得注意的就是我添加了 DEBUG 参数,这会产生一个带有监测内存泄漏参数版本的 Makefile。
所以接下来只需要生成 Makefile
$ cmake -DDEBUG=1 .然后编译我们的代码
$ make编译后得到名为 sol 的可执行程序,我们可以运行他来启动我们的 broker,程序支持我们上面编写的那些参数。
我们通过 -v (verbose) 参数启动程序,这样可以看到 debug 级别的日志信息。
$ sol -v结尾
好了,到此为止就是这么多内容,现在我们的代码也许有很多bug,有内存泄露问题,有很多需要修复或者重构的代码,但是软件的框架就是这样子了。第七部分很快就会编写完成,我打算用 paho-mqtt 进行一些测试。接下来你可以看看特别篇,在那里我们会为 sol 添加多线程支持。